Dillon, Patrick B.1 and Fonseca, Fernando S.2
1 Staff Engineer II, WDP & Associates Consulting Engineers, Inc., 335 Greenbrier Dr., Suite 205, Charlottesville, VA, 22901, USA, pdillon@wdpa.com
2 Associate Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Brigham Young University, Provo, UT 84602, USA, fonseca@byu.edu
ABSTRACT
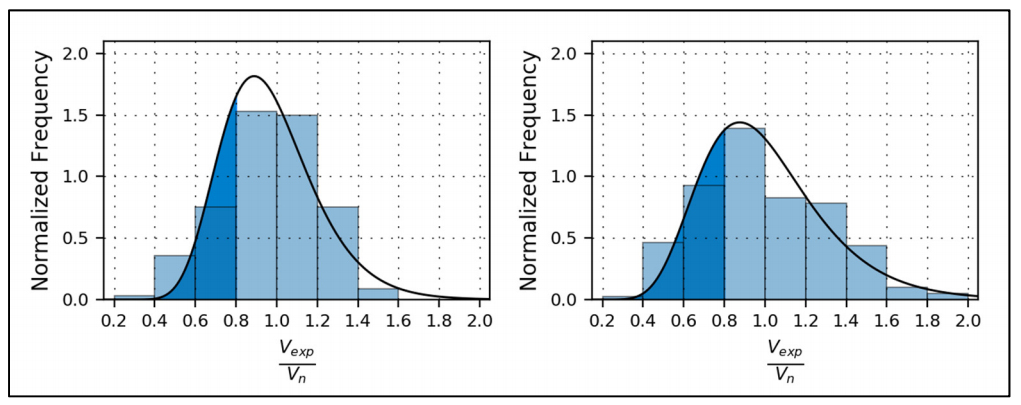
A dataset of 167 fully and 205 partially grouted masonry shear wall specimens was recently assembled. The combined dataset of 372 masonry shear wall test results has been used to perform regression analysis to determine the accuracy and precision of the TMS masonry shear strength equations. The analysis confirmed previous observations that the TMS shear equation is unconservative for partially grouted shear walls. Additional analysis was conducted to investigate the effectiveness of the grouted wall factor recently introduced into the TMS shear equation. The analysis also indicated that the shear equation demonstrates more variability for partially grouted walls than for fully grouted walls, and it appears that the increased variability has gone unnoticed when considering the shear strength of partially grouted masonry. This article presents a statistical analysis of the modeling uncertainties for fully and partially grouted masonry shear walls. The analysis shows that the current shear strength equations in TMS and CSA predict design strengths that are more variable for partially grouted walls than for fully grouted walls. The increase in variability is due to a bias in the current equations toward fully grouted walls because they were developed using fully grouted wall data. Corrections are recommended for the TMS and CSA shear strength equations to reduce the difference in accuracy and uncertainty between partially grouted and fully grouted masonry.
093