1 Research Engineer, National Concrete Masonry Association 2302 Horse Pen Road, Herndon VA 20171-3499
2 Associate Professor, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering Washington State University, Pullman, WA 99164-2910
3 President, Northwest Concrete Masonry Association 40 Lake Bellevue, Suite 100, Bellevue, WA 98005-2480
ABSTRACT
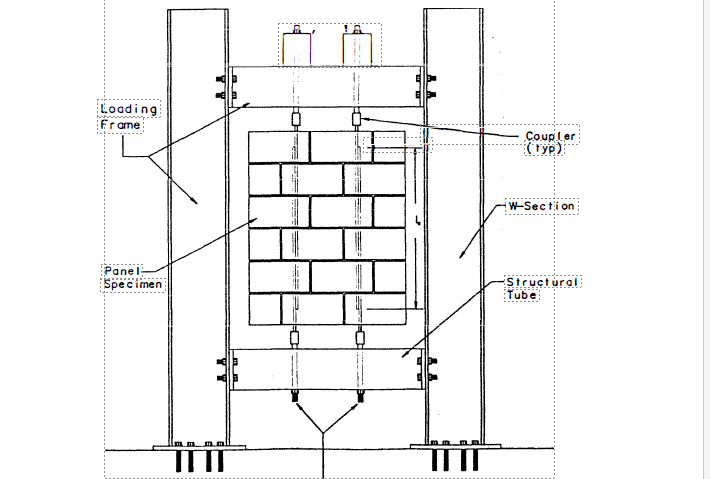
Experimental tests were conducted on 25 specimens consisting of203-mm (8-inch) concrete block walls incorporating· lap splices of No. 5 and No. 7 reinforcing bars. The lapped bars in each of the specimens were loaded in tension until failure occurred. Test results showed that current code specifications for lap splices overestimated the required lap for the smaller size bars and underestimated the required lap for the larger bars. The experimental results of this study were combined with the results from other research efforts investigating the performance of lap splices in concrete masonry. It was found that the reinforcement diameter, clear cover, and masonry compressive strength had a significant effect on the required length of lap for splices. A new design equation is proposed which more accurately represents the observed performance of tension lap splices in reinforced concrete masonry.
2478.pdf