- M. Reda Taha1, A. S. El-Dieb2, and N. G. Shrive3
ABSTRACT
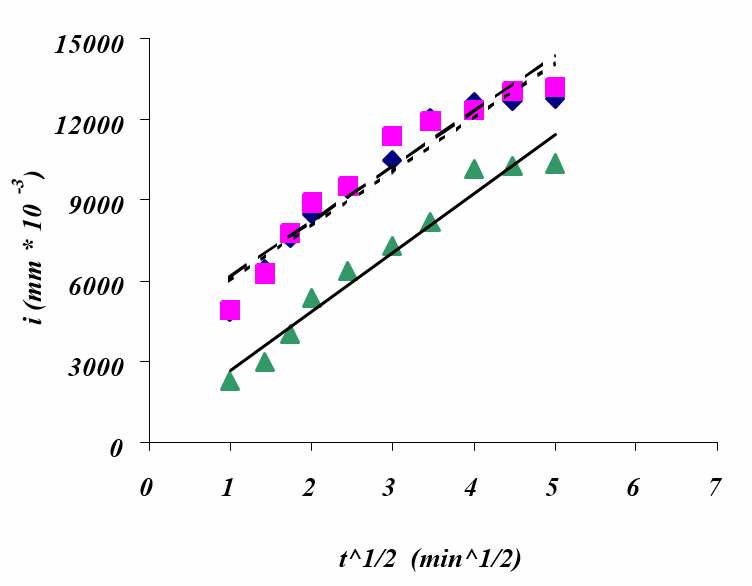
Surface absorption of brick units has a significant effect on masonry bond. Therefore, a reliable and reproducible method should be used to measure the surface absorption of masonry units and establish acceptability criteria. Some codes assess absorption properties through the initial rate of absorption (IRA): others use total absorption. During the last 50 years, different research work has revealed that IRA is an inconsistent measure of the surface absorption of masonry units in relation to subsequent bond. Current measurements of the surface absorption of brick units are therefore reviewed critically. The theoretical basis of sorptivity as a measurement of surface absorption is presented. An experimental programme, incorporating different brick units, was executed to examine the sorptivity of masonry brick units. Analysis of the experimental results showed sorptivity to be a reliable and a
reproducible engineering measurement for predicting the surface absorption performance of brick units. Statistical analysis and comparisons to other surface absorption measurements are developed. Sorptivity should be considered for the Canadian masonry standard as the surface absorption criterion for masonry brick units.
Key words: Masonry Bond, Surface Absorption, Sorptivity, Permeation and Total absorption
Bmoist04