- F. da Porto1, F. Mosele2 and C. Modena3
1Assistant Professor, 2 Ph.D. Candidate, 3Full Professor
Department of Structural and Transportation Engineering, University of Padova, Italy daporto@dic.unipd.it, mosele@dic.unipd.it, modena@dic.unipd.it
ABSTRACT
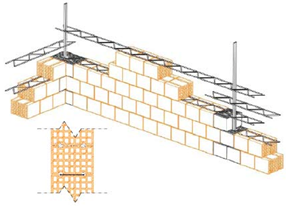
In the framework of the DISWall project, funded by the European Commission, innovative construction systems for reinforced masonry walls were developed for the application in seismic areas. In particular, a new reinforced masonry system made with horizontally perforated clay units was developed on purpose for typical low-rise residential buildings to withstand in-plane actions. Thirty specimens of this type of masonry were characterized by means of uniaxial tests and by means of in-plane cyclic shear compression tests. The tests were carried out on either specimens with horizontal rebar reinforcement or truss reinforcement. Furthermore, the in-plane cyclic tests were carried out on both slender and squat specimens, under different precompression levels, in order to force both flexural and shear failure mechanisms. In the present contribution, the results of the cyclic tests carried out are discussed. Data of steel strain on rebars and trusses, ductility parameters, energy dissipation, stiffness degradation are discussed.
KEYWORDS: reinforced masonry; in-plane cyclic tests; strength; steel strain; ductility; energy dissipation; stiffness degradation.
PDF file A1-2