T.F.T. Silva1, M.A. Ramalho2 and M.R.S. Corrêa3
- Master Student, Dept of Structures, University of São Paulo, Brazil, tftsilva@yahoo.com.br
- Associated Professor, Dept of Structures, University of São Paulo, Brazil, ramalho@sc.usp.br
- Associated Professor, Dept of Structures, University of São Paulo, Brazil, mcorrea@sc.usp.br
ABSTRACT
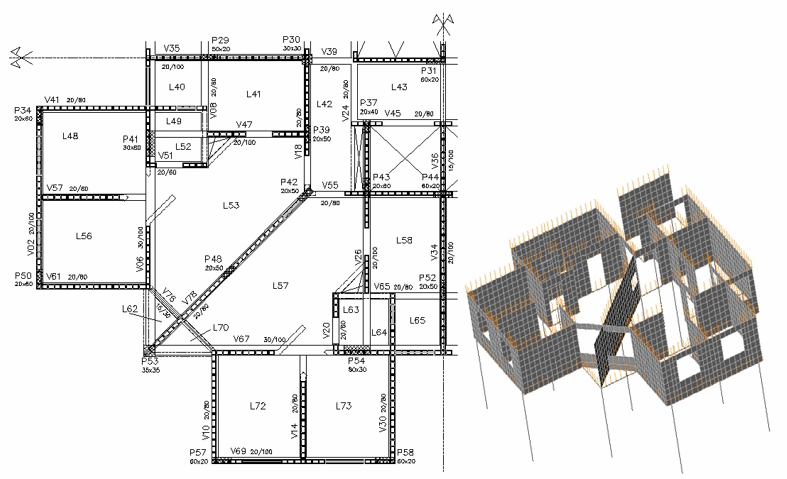
The so-called arch effect is very important for evaluating stresses and internal forces at interfaces between structural masonry and reinforced concrete structures. The arch action induces stress concentrations in stiffer regions and relief where the stiffness is lower. This can be harmful for masonry over the supports however it may cause a significant reduction in the internal forces of concrete beams, mainly the bending moments. This paper presents a proposal for a numerical analysis procedure for the masonry/concrete interface using the finite element method. Its main feature is to be suitable for design purposes because it is simple and can be run on small computers. Despite its simplicity, the obtained results are adequate in terms of simulating the stress concentration on the masonry walls and the internal force reduction in concrete beams. Initially, some concepts of the arch effect and the theoretical basis for the proposed analysis procedure are presented. Afterwards, some details on the design of this kind of structure are discussed in order to highlight the main aspects that should be observed. Finally, results for three residential building cases are presented, emphasizing the differences obtained between the proposed procedure and the usual way of considering the structural masonry and reinforced concrete interaction.
KEYWORDS: arch effect, structural interaction, Finite Element Method, structural masonry.
3c-2