Department of structural and architectural design
Eindhoven University of Technology. Postbus 513, 5600 MB, Eindhoven
The Netherlands
ABSTRACT
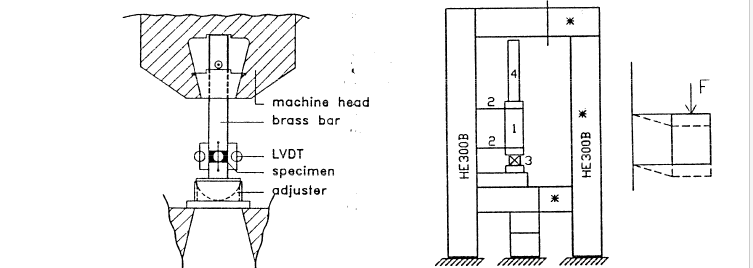
Test pieces made form mortar that hardened between bricks are more representative for mortar behaviour in masonry than specimens made in steel moulds. Cylinders and square prisms were cut out of slices of mortar hardened between bricks, having a thickness of at most 15 mm because this is the largest bed joint thickness commonly used. To test these small sized mortar specimens a press was modified in two different ways and the behaviour of the modifications was investigated.
The effects of capping materials and of teflon layers between cylinder and platens, the position of the cylinder in the mortar slab before drilling and the effect of moisture conditions of the bricks on the mortar were studied. Tendencies of these various experimental details on strength and stiffness were found. However, subsequent research into the large variation of the properties using ESPI is required. Results can be used in numerical simulations.
9008.pdf