Sagar, S. Lalit1; Singhal, Vaibhav2 and Rai, Durgesh C.3
1 Former Graduate Student, Dept. of Civil Eng, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur, UP, India, lalithsagar@gmail.com
2 Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil and Envn. Eng., Indian Institute of Technology Patna, Bihta, Bihar, India, singhal@iitp.ac.in
3 Professor, Dept. of Civil Eng., Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur, UP, India, dcrai@iitk.ac.in
ABSTRACT
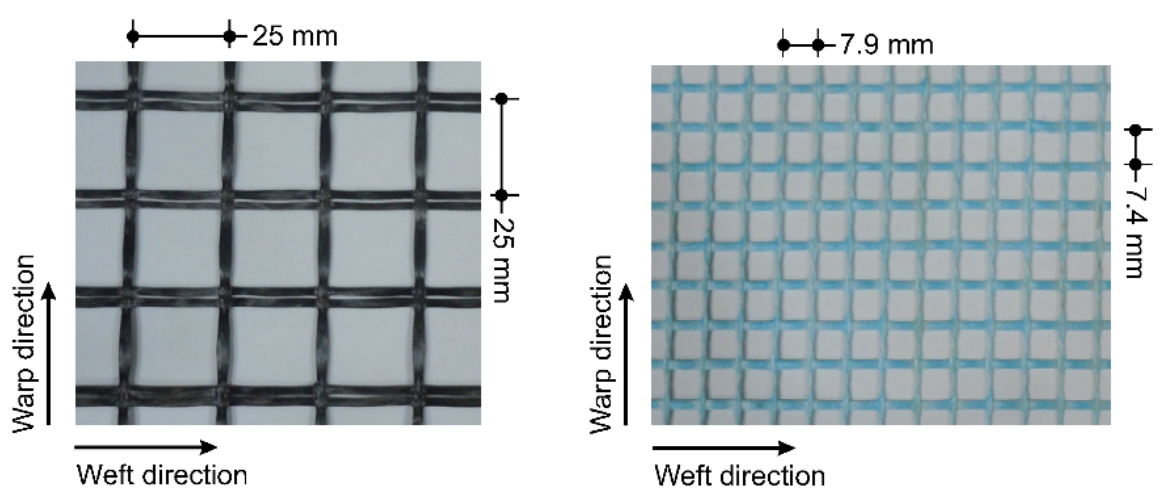
The efficacy of a composite overlay known as Fabric Reinforced Cementitious Matrix (FRCM) was assessed for seismic strengthening of masonry infill walls in the present experimental program. Six half-scale masonry infilled RC frames with different FRCM configurations were tested to study the effect of method of the fabric application, provision of mechanical anchors and orientation of the fabric on the performance of the strengthened infill walls. Two methods of fabric application were employed to examine the effect on FRCM: direct application and sandwich application. A unique loading protocol was used for bi-directional loading of the specimen, consisting of successive application of slow cyclic drifts for in-plane loading and shake-table generated ground motion for out-of-plane loading. The strengthened infill walls could safely withstand a storey drift in excess of 2.20%, preserving the structural integrity without jeopardizing its out-of-plane capacity. The direct mode of application of the fabric exhibited a superior performance with better bond characteristics and stress redistribution. The mechanical anchors were effective in limiting the separation of the infill from the frame, resulting in enhanced bi-directional response. The orthogonal orientation of the fabric was more effective compared to the oblique orientation for FRCM strengthening.
064