Sparling, Adrien1; Palermo, Dan2 and Hashemian, Fariborz3
1 PhD Student, Civil Engineering, York University, 4700 Keele St., Toronto, ON, Canada, adriensp@yorku.ca
2 Associate Professor, Civil Engineering, York University, 4700 Keele St., Toronto, ON, Canada, dan.palermo@lassonde.yorku.ca
3 Adjunct Professor, Civil Engineering, York University, 4700 Keele St., Toronto, ON, Canada, fariborz.khaleghihashemian@pc.gc.ca
ABSTRACT
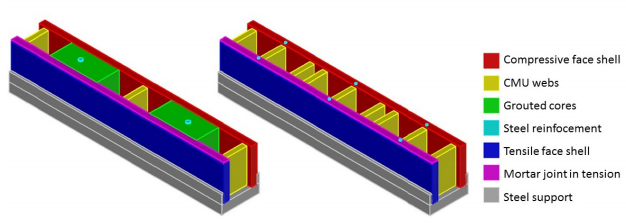
In recent decades the use of conventional masonry in the area of light industrial warehouse construction has been replaced by other materials. This is attributed, in part, to the high cost of stiffening elements (i.e. columns or pilasters) required for the construction of freestanding masonry walls. The innovative Surface-Reinforced Concrete Masonry Unit (SRCMU) system, incorporating near-surface mounted (NSM) reinforcement, has demonstrated the potential to address current challenges in conventional masonry construction by enabling the construction of lighter and stiffer walls without requiring stiffening elements. SRCMUs are hollow concrete blocks that contain vertical groves on their exterior faces, allowing reinforcing bars to be placed near the extreme tension fibre of walls subjected to out-of-plane loads. To this end, a series of four masonry walls were recently constructed for testing under conditions of third-point flexural loading. The walls were constructed from 200 mm (nominal) hollow concrete masonry units, and have a width of 1.2 m and height of 3.2 m. Each wall contains the same gross vertical reinforcement ratio of 0.26%. The objective of the testing program is to isolate and determine the effect of grouting as well as that of reinforcing bar placement on out-of-plane flexural behaviour. Finite element analyses of NSM reinforced SRCMU walls are presented herein to illustrate the anticipated benefits of this system over conventional reinforced masonry.
089