Jeffrey H. Greenwald, P.E.1, Jason J. Thompson2 and David I. McLean, Ph.D., P.E.3
- Vice President of Research and Development, National Concrete Masonry Association,
- Structural Engineer, National Concrete Masonry Association,
- Professor, Washington State University
ABSTRACT
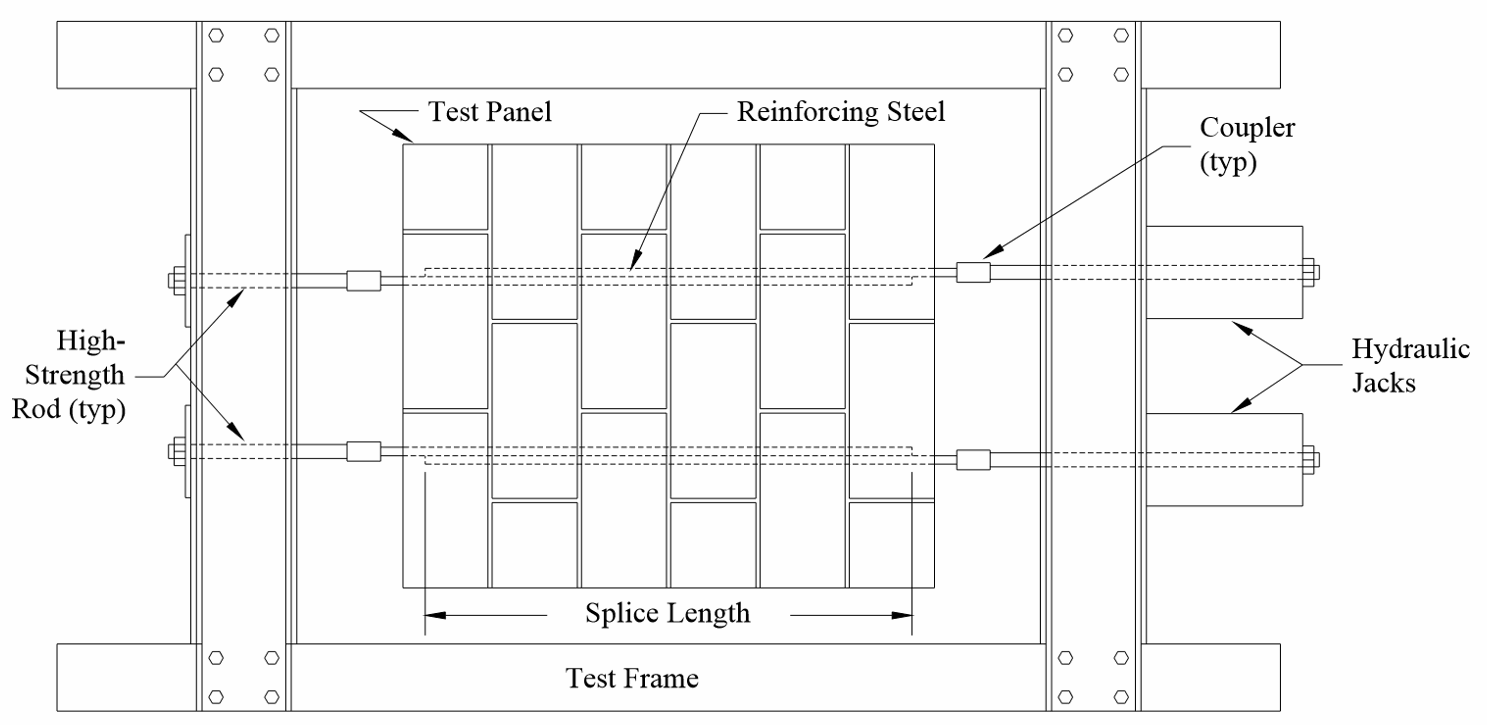
This paper reports on research to investigate the effects of confinement provided by lateral reinforcement on lap splice performance. Fifteen concrete masonry panels were constructed using 200 mm (8-in.) units. Two sets of 25M (No. 8) lap spliced reinforcing bars were placed in each specimen. A lap length of 1200 mm (48 in.) was used for each splice tested in this study. To evaluate the effects of confinement reinforcement on splice behavior, five different arrangements of lateral reinforcement in the panels were considered: no transverse reinforcement, one 10M (No. 4) bar near each end of the splice, two 10M (No. 4) bars near each end of the splice, one 10M (No. 4) bar in each course of the panel, and two 10M (No. 4) bars in each course of the panel. The spliced bars were loaded in direct tension to determine the capacity of the splice. Test results show that bar reinforcement placed transversely to a splice is effective at providing some degree of confinement and results in significantly improved performance and increased splice strength.
KEYWORDS: concrete masonry, reinforcement, splices, laps, confinement
6c-4