Mohamed Zorainy, Ahmed Ashour, Obaidat Ala’ T. and Khaled Galal
Mohamed Zorainy, Former M.A.Sc. Student, Department of Building, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Concordia University, 1515 St. Catherine West, Montreal, QC, Canada. Currently, Assistant Lecturer in the Department of Civil Engineering, Ain Shams University, Cairo, Egypt, mohamed.yosry@eng.asu.edu.eg
Ahmed Ashour, Assistant Professor, Department of Structural Engineering, Cairo University, Cairo University Rd, 12613, Egypt, dr.ashour.ahmed@gmail.com
Obaidat Ala’ T., Former PhD graduate, Department of Building, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Concordia University, 1515 St. Catherine West, Montreal, QC, Canada. Currently, Assistant Professor in the Faculty of Engineering, Philadelphia University, Jordan, aobaidat@philadelphia.edu.jo
Khaled Galal, Professor, Department of Building, Civil and Environmental Engineering, Concordia University, 1515 St. Catherine West, Montreal, QC, Canada, khaled.galal@concordia.ca
ABSTRACT
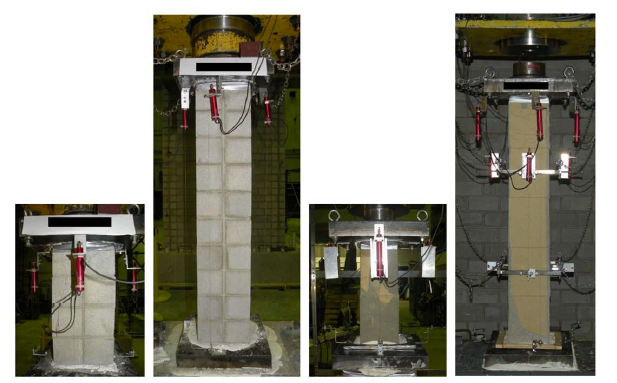
Reinforced masonry shear walls (RMSW) with masonry boundary elements (MBE) are rectangular walls with integrated MBEs at the wall extremities. The compressive stress-strain behaviour of the MBE prisms built using C-shaped blocks (C-MBEPs) varies from that of regular stretcher prisms due to the continuity of the grout core and the higher grout-to-shell area ratio. Few studies have investigated the stress-strain behaviour of MBEs built using C-shaped blocks. This study evaluates the compressive stress-strain behaviour of half-scale fully grouted C-MBEP and its constituents (i.e., masonry shell and grout core). In total, 8 fully grouted masonry prisms, 6 un-grouted masonry shells, and 18 grout cores were tested under concentric displacement-controlled compression loading. The test matrix is composed of two aspect ratios: two and five, and normal and high grout strengths. In addition, the effect of grout core treatment, i.e., air and wet treatment, was examined. Similar to masonry prisms made from stretcher blocks, the superposition of the load-displacement relationship of the grout core and the masonry shell was found not comparable to that of the grouted C-MBEP Prisms built with similar grout and masonry blocks.
KEYWORDS: C-shaped blocks, grout, height-to-thickness ratio, masonry boundary element, stress-strain behaviour, superposition