Bansal, Nitin1 and Rai, Durgesh.C.2
1 Frm. Graduate Student, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India, nitinbansal64@gmail.com
2 Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur, Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, India, dcrai@iitk.ac.in
ABSTRACT
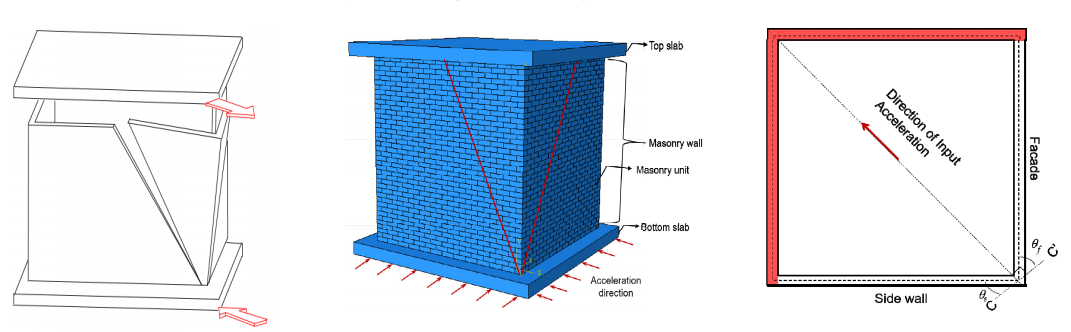
Majority of the masonry research work deals with its failure due to either in-plane (IP) or out-ofplane (OP) lateral forces. However, failure of masonry walls at corners, though frequent, has not been researched much. Such failure involves the detachment of a wedge shaped portion of masonry from the corner walls under the action of bidirectional lateral load. Behaviour of corners in dry stack masonry was studied up to failure in ABAQUS, Finite Element (FE) environment using explicit solver. Various models of masonry structures with loadbearing and non-loadbearing walls were considered and were subjected to dynamic loading along the corner. Based on the failure pattern observed under the simultaneous action of IP and OP forces, simplified corner failure mechanisms were proposed for the limiting equilibrium condition and corresponding values of peak acceleration were obtained. Results of limit analysis compared well with FE predictions. The FE approach adopted for dry stack masonry was extended to study the corner failure in mortar bonded masonry. A distinct friction coefficient for each course was introduced which was equivalent to the shear resisted by the layer of mortar in any given course. Such a method of modelling was effective in determining the propagation of cracks through the masonry as well as the value of acceleration at which a portion of corner wall detaches from the rest of the masonry. This study not only helped in understanding the failure pattern of corner masonry walls, but also provided an approach to estimate the limit strength in terms of peak acceleration.
067