1 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran. shakib@modares.ac.ir
2 Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran.
3 Department of Civil Engineering, Sharif University, Iran
4 Director of the Research Bureau, Tehran Province Gas Company, Tehran, Iran.
ABSTRACT
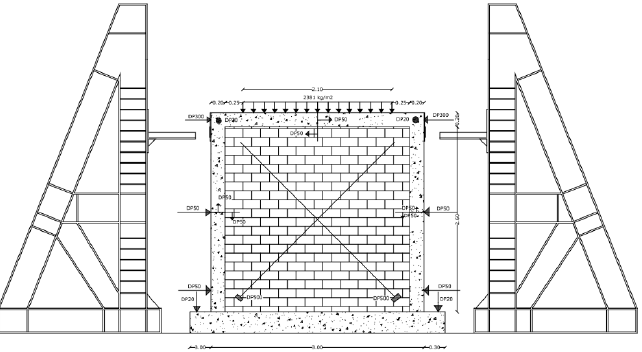
Masonry structures are widely used due to its available materials, low cost and construction easiness. Every year large casualties due to collapse of masonry buildings during earthquakes are reported. So many of the existing unreinforced masonry (URM) buildings are seismically vulnerable and need to be retrofitted.This paper presents experimental and analytical results of in-plane behaviour of URM walls retrofitted using shotcrete and carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP).The experimental program consists of testing three URM walls. A traditional wall was tested as the reference. Another one was retrofitted by using a 50 mm thick layer of shotcrete on one side. The last wall was retrofitted by using CFRP composites, on one side. The traditional wall consists of a single–story clay brick panel confined by RC bond-beams and tie-columns. The RC members are assumed to be of the concrete with a compressive strength equal to 12 MPa. The lower RC bond–beam is restrained against horizontal and vertical displacements. However, the upper one transfers static monotonic lateral displacement load. In this study all of the samples are tested at an age of 28 days. Analytical studies are performed with macro modelling and tested walls are calibrated with the analytical model. The comparison of these retrofitting techniques in terms of capacity, implementation and cost showed the superiority of the shotcrete technique over the other alternative.
KEYWORDS: seismic retrofitting, unreinforced masonry, cyclic test, CFRP, shotcrete, macro model
607.pdf