Lu, Xilin1; Li, Xin2; Zhou, Bin 3 and Ren, Xiaosong 4
1 Professor, Research Institute of Structural Engineering and Disaster Reduction, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China, lxlst@tongji.edu.cn
2 Ph.D., Research Institute of Structural Engineering and Disaster Reduction, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China, 2010lixin@tongji.edu.cn
3 D.E., Tongji Architectural Design (Group) Co., Ltd, Shanghai 200092, China, ebinzb@163.com
4 Professor, Research Institute of Structural Engineering and Disaster Reduction, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China, rxs@tongji.edu.cn
ABSTRACT
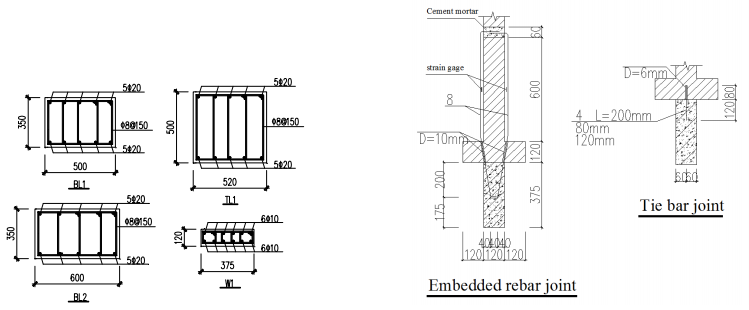
Masonry structures are widely used in residential and public architectures, especially some seismic regions in China before the 1990s. The failure of masonry structures is influenced by several factors, e.g. material properties of brick and mortar, geometry of brick, joint thickness, properties of bond of brick and mortar, etc. These masonry structures, built in early stage, cannot satisfy the seismic requirement. Retrofitting existing masonry structures by installing the reinforced concrete members around the masonry structure is a new retrofit method. This method can not only improve the strength, but also improve the stiffness of the masonry structures. The longitudinal and the transverse composite walls were constructed under cyclic loading test. The test specimens were composed by masonry wall and RC element. The ultimate bearing capacity, ductility, hysteresis characteristic, stiffness degradation and damage pattern are analyzed in this paper. The conclusions are as follows: the connecting joint, pull (shear) bar and embedded bar, presented in this paper, have good connection capacity. The composite wall has good capacity of load bearing and deformation. By the analysis of equivalent viscous damping coefficients, the energy dissipation capacity of masonry wall is improved by post-installed concrete wall.
044