Oliveira1, J. Casali2 and L. R. Prudêncio Jr3.
- Federal Center of Technological Education of Santa Catarina, DCC, Florianópolis/SC, Brazil, alexandre@cefetsc.edu.br
- Federal University of Santa Catarina, Civil Engineering Department, Florianópolis/SC, Brazil, jucasali@hotmail.com
- Federal University of Santa Catarina, Civil Engineering Department, Florianópolis/SC, Brazil, prudenciouk@hotmail.com
ABSTRACT
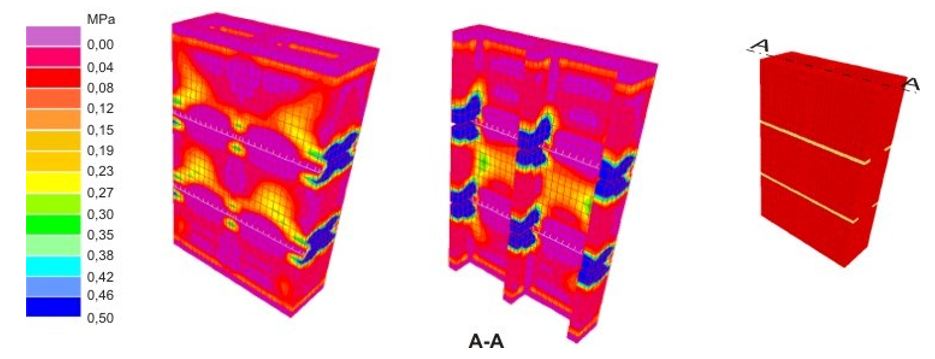
In southern Brazil, one type of hollow concrete block is typically employed in structural masonry constructions. Its dimensions are 140 x 190 x 390 mm (width x height x length), which is not a modular size (its nominal length [400 mm] is not a multiple of its nominal thickness [150 mm]). What is more, the block’s geometry does not allow superimposition with perfect alignment of its cores; this produces stress concentration in structural masonry walls. In this context, this work proposes a new type of hollow concrete block (140x190x440 mm), which does allow full alignment of the cores. The behaviour of masonry prisms and wallettes was evaluated, for both types of blocks, using finite element (FE) modelling. Linear elastic FE analyses were carried out by modelling the prisms and wallettes with a fine mesh of solid elements, and by taking into account the positions of the cores as well as the mortar bedding pattern (face-shell bedding and full mortar bedding). The results of the numerical analyses show that, with face-shell bedding, the levels of stress in the prisms and wallettes are very similar for the two types of blocks. However, with full mortar bedding, while the stress levels in the prisms are also very similar for the two types of blocks, the new type of concrete block has the best structural performance in the wallettes, with lower levels of stress, due to a better alignment of the cores allowed by this new type of concrete block.
KEYWORDS: concrete blocks, finite element, linear elastic, prisms, wallettes, face shell bedding and full mortar bedding
A4-4