El-Hashimy, Tarek1; Campidelli, Manuel2; Tait, Michael3 and El-Dakhakhni, Wael4
1 Ph.D. Student, Department of Civil Engineering, McMaster University, 1280 Main St. West, Hamilton, ON, Canada, elhashth@mcmaster.ca
2 Research Coordinator, Department of Civil Engineering, McMaster University 1280 Main St. West Hamilton, ON, Canada, campide@mcmmaster.ca
3 Professor and Chair, Department of Civil Engineering, McMaster University 1280 Main St. West Hamilton, ON, Canada, taitm@mcmaster.ca
4 Professor, Martini, Mascarin and George Chair in Masonry Design, Department of Civil Engineering, McMaster University 1280 Main St. West Hamilton, ON, Canada, eldak@mcmaster.ca
ABSTRACT
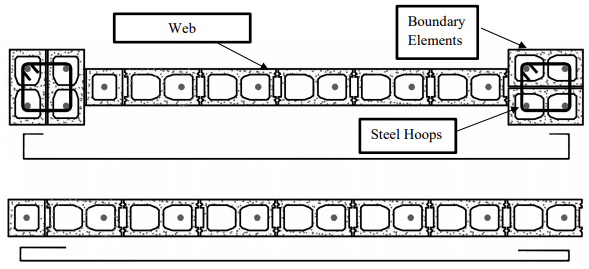
Boundary elements (BEs) have been shown to enhance the in-plane performance of reinforced masonry (RM) walls, in terms of both section capacity and ductility. For this reason, in 2014 these elements were introduced in the Canadian standard S304-14 as a seismic force resisting system. When their out-of-plane performance is considered, BEs can significantly increase the loadbearing capacity of RM shear walls when subjected to blast overpressure from live explosives. However, the mechanism by which the wall capacity is affected is still unclear. To shed some light on this problem, a BE-wall was tested statically by the authors to examine the interaction between BEs and the web as well as the change in wall’s stiffness beyond its elastic range. In this investigation, two approaches are proposed to model the post-elastic stiffness of the test specimen and their predictive capabilities are discussed on the basis of data from static testing. Furthermore, a single degree-of-freedom model is used to simulate the maximum out-of-plane displacement experienced by the same wall when subjected to blast overpressure. The numerical results are compared to data from field testing of nominally identical BE-walls, to verify the adequacy of the adopted model. The current study contributes to the growing understanding of BEs’ influence on the deformation of the wall central panel.
053