M.A. ElGawady1, P. Lestuzzi2, and M. Badoux3
- Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Auckland, Private Bag 92019, Auckland, New Zealand, melg003@ec.auckland.ac.nz
- IMAC Applied Computing and Mechanics Laboratory, School of Architecture, Civil, and Environmental Engineering ENAC, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology at Lausanne EPFL, pierino.lestuzzi@epfl.ch.
- Former IS-Beton, ENAC, EPFL, marc.badoux@epfl.ch
ABSTRACT
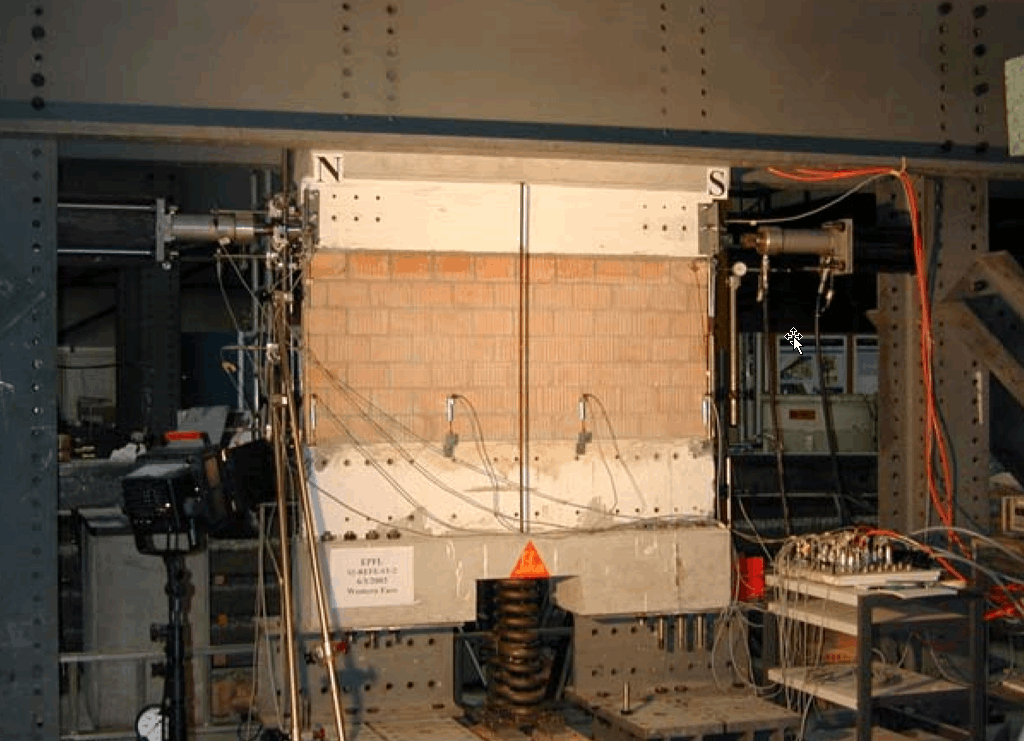
An extensive research program for retrofitting of unreinforced masonry (URM) walls has been carried out in Switzerland. The program included in-plane dynamic and static cyclic tests on URM walls retrofitted using composites, post-tensioning, and shotcrete. This paper presents part of the preliminary test results of the static cyclic tests. Five half-scale walls were built using half-
scale hollow clay masonry units and weak mortar. The specimens had two effective moment/shear ratios: 0.50 and 0.67. The specimens, before and after retrofitting, were subjected to a series of force and displacement control test runs. For specimens with effective moment/shear ratio of 0.50, the test showed that fiber reinforced polymers improve the lateral resistance as much as 6 times the lateral resistance of the reference specimens. In addition, applying post-tensioning was equivalent to retrofitting the specimens using one layer of glass fiber reinforced polymers. For specimens with effective moment/shear ratio of 0.67, composites improved the lateral resistance as much as 2.5 times the lateral resistance of the reference specimen.
KEYWORDS: retrofitting, strengthening, earthquake, static cyclic, composites, fiber.
5b-1