Maqsud E Nazar1 and S.N. Sinha2
1Managing Director, NNC Consultant Pvt. Ltd., B-2, Jaswant Chambers, Okhla, Jamia Nagar, New Delhi-110025, India.
2Professor, Civil Engg. Department, Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, New Delhi-110016, India.
ABSTRACT
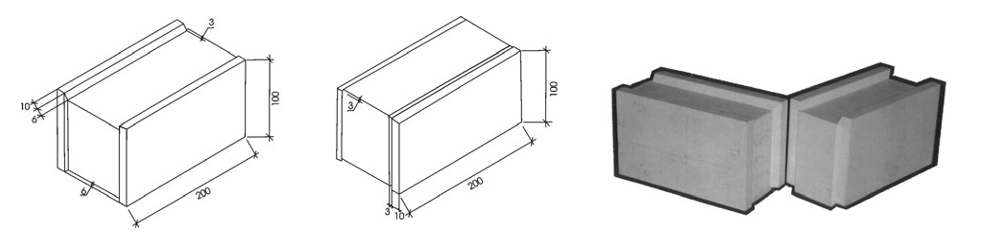
A series of laboratory tests has been conducted to investigate the influence of bed joint orientation on interlocking grouted stabilised sand-flyash brick masonry under cyclic compressive loading. Five cases of loading at 00, 22.50, 450, 67.50 and 900 with the bed joints are considered. The brick units and masonry system developed by Prof. S.N. Sinha is used in present investigation. Eighteen specimens of size 500 mm x 100 mm x 700 mm (19.68 in. x 3.94 in. x 27.55 in.) and twenty seven specimens of size 500 mm x 100 mm x 500 mm (19.68 in. x 3.94 in. x 19.68 in.) are tested. The loops of stress-strain hysterisis obtained from cyclic loading tests have been used to determine the energy dissipation characteristics of interlocking grouted stabilised sand-flyash brick masonry. The variation of envelope strain, common point strain and stability point strain with plastic strain has been plotted. A polynomial formulation is proposed for the relations between energy dissipation ratio versus envelope strain and energy dissipation ratio versus residual strain. These relations indicates that the decay of masonry strength starts at about 0.42 to 0.75 times of peak stress depending upon the load case.
KEYWORDS: Interlocking brick, grout, uniaxial, cyclic loading, envelope curve, common point, stability point, stress-strain hysteresis
B6-2